Matching Software Requirements to Git Artifacts
Matching Software Requirements to Git Artifacts
2022 SURF Abstract by Sonora Halili, Anisha Jain, and Joey Elsbernd
Imagine leaving a dinner party hungry. Although your friend took note of each guest’s dietary needs, they failed to account for each of them while grocery shopping, unintentionally leaving you with no options. Now imagine a tool that could remind your friend after each purchase that you can’t have gluten, and that your other friend can’t have dairy, or that your other friend is vegetarian. This would narrow down the recipe options for the host. They’d need to decide whether it’s worth cooking three separate meals or one complex dish instead. Eventually, the decision would have to please everyone.
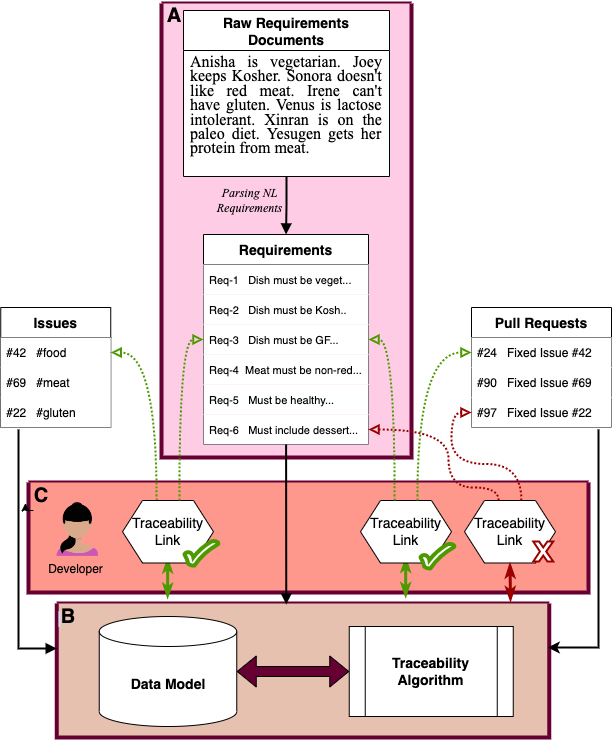
Software development is our favorite dinner party. There may be many cooks and many recipes, but it is of utmost importance that everyone gets to eat. The dietary specifications of software development are requirements––clear-cut expectations for the final product. Requirements Management (RM) refines the coding workflow, yielding quality bespoke software. RM techniques include creating traceability links between requirements and development artifacts (i.e., issues and pull requests), an often costly task that developers are reluctant to invest in. Completing this process manually is tedious and time-consuming, given that even small and medium-scale projects come with hundreds of requirements. In this project, we investigated the feasibility of creating a lightweight, open-source, Git-based tool that can complete the mapping process semi-automatically, reducing both the time and monetary cost of fully integrating RM.
Our proposed tool will take in requirements in natural language (plain text), map them to existing Git artifacts (issues and pull requests) through Natural Language Processing (NLP), and prompt the user to select among the suggested traceability links. It will function iteratively, allowing the user to update and add links at all stages of the development process. The Git development environment is ubiquitous for small and medium sized companies, so hosting our solution through existing Git infrastructure will make RM more accessible in the software development community.
We explored cloud-based Git repository websites (GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab) and chose to extend the GitLab interface, given that it is open-source and comes with a barebones requirements feature. Additionally, Smith College Computing and Technical Services (CATS) runs a local version of GitLab and agreed to host our improvements. In future works, we will continue to research NLP techniques and Deep Learning techniques for connecting requirements with Git artifacts.